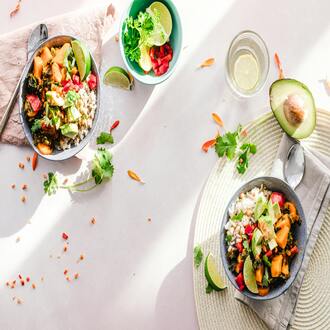Transcription Standard ketogenic diet (Skd)
The standard ketogenic diet, commonly referred to as the SKD (Standard Ketogenic Diet), is one of the most popular and widely used variants of the ketogenic diet. It is a nutritional approach that relies on a high intake of healthy fats, a moderate intake of protein, and a significant restriction of carbohydrates.
In this session, we will explore in detail what the standard ketogenic diet is, how it is carried out, and what its benefits and considerations are.
Fundamental Principles of the Standard Ketogenic Diet
The SKD is based on drastically reducing carbohydrate intake to induce a state of ketosis. By limiting the availability of carbohydrates, the body is forced to turn to fat stores as the primary source of energy. During this process, the liver produces ketones, which are energy molecules derived from fats. Ketosis is the key metabolic state sought in SKD.
In SKD, the macronutrient ratio is usually approximately 70-75% fat, 20-25% protein and less than 5% carbohydrate. This ratio ensures that carbohydrate intake is low enough to maintain ketosis, while fats and proteins provide the necessary energy and protect muscle mass.
Foods allowed on the standard ketogenic diet
The SKD focuses on foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, coconut oil, olive oil, nuts and seeds, butter and animal fats. Also included are high-quality proteins, such as lean meats, fish and seafood, eggs and low-carbohydrate dairy products. Non-starchy vegetables, such as spinach, broccoli and cauliflower, are an essential part of the SKD because of their low carbohydrate content.
Benefits of the standard ketogenic diet
The SKD has demonstrated several health and wellness benefits. One of the most prominent benefits is weight loss, as the body uses stored fats as a source of energy, resulting in a reduction of adipose tissue.
In addition, ketosis can improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance. In addition, some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet may have positive effects on brain function and cognitive performance.
Considerations and Precautions
Although the SKD may be effective for many people, it is not suitable for everyone. Some people may experience temporary side effects, such as fatigue, dizziness, or bad breath (known as ketonic breath).
In addition, people with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, should avoid the ketogenic diet without medical supervision. It is also important to make sure to maintain adequate vitamin and mineral intake through a variety of foods allowed on the SKD.
Establishing a Ketogenic Eating Plan
To successfully follow the SKD, it is important to carefully plan meals and food choices. It is helpful to keep track of macronutrient intake and use apps or online tools to calculate and monitor carbohydrate, protein and fat intake. This will ensure that you stay within the right range to achieve and maintain ketosis.
Staying well hydrated is essential on the ketogenic diet. Since the SKD can have a diuretic effect, it is easy to lose fluids and electrolytes. Drinking enough water and consuming foods rich in potassium, magnesium, and sodium can help maintain proper electrolyte balance. In addition, regular physical activity is beneficial for optimizing SKD results, improving body composition and endurance, and maintaining overall health.
standard ketogenic diet